Mercedes-Benz is pursuing a holistic approach to the circularity of battery systems, with consideration given to three core topics: circular design, value preservation, closing the cycle.
,xPosition=0,yPosition=0.5)
Circular economy of battery systems
Mercedes-Benz AG
Mercedesstraße 120
70372 Stuttgart
Germany
Phone: +49 7 11 17-0
E-Mail: dialog@mercedes-benz.com
Please send queries about content on this website to any contact. You can address your concerns to us in English and your respective national language.
Represented by the Board of Management:
Ola Källenius, Chairman; Jörg Burzer, Renata Jungo Brüngger, Mathias Geisen, Markus Schäfer, Olaf Schick, Britta Seeger, Oliver Thöne, Harald Wilhelm
Chairman of the Supervisory Board: Martin Brudermüller
Court of Registry: Stuttgart; commercial register no. 762873
VAT ID: DE 32 12 81 763
All information about our products can be found on your country-specific Mercedes-Benz product page.
,xPosition=0,yPosition=0.5)
Circular economy of battery systems
Mercedes-Benz is pursuing a holistic approach to the circularity of battery systems, with consideration given to three core topics: circular design, value preservation, closing the cycle.
Mercedes-Benz is consistently creating the conditions for a net carbon-neutral
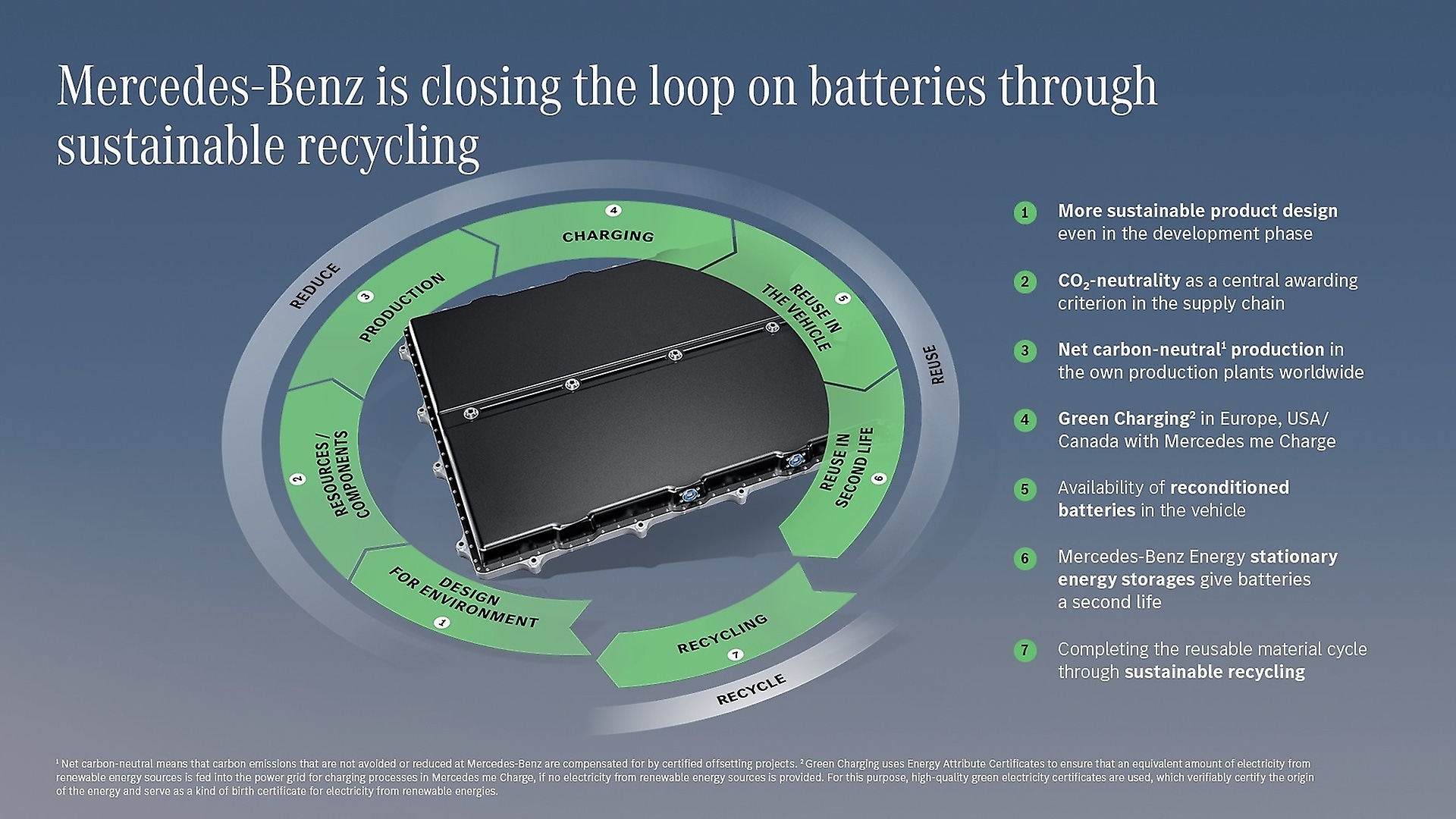
We are thinking about the circular economy right from the start in product development. This also applies to battery technology. During the development of a vehicle, we create a concept for each model in which all components and materials are analysed for their suitability as part of a circular economy. It is checked to what extent the components and materials are suitable for the various stages of the recycling process, including the material recycling of the battery raw materials used. As part of the analysis, the entire value chain is considered - from the mine to recycling. For the Mercedes-Benz Group, as a fundamental part of responsible corporate governance, this includes respect for human rights in the working conditions of employees at our suppliers. With the Human Rights Respect System (HRRS), the Group has developed an approach for implementing human rights due diligence to meet its aspirations. In addition, our Responsible Sourcing Standards

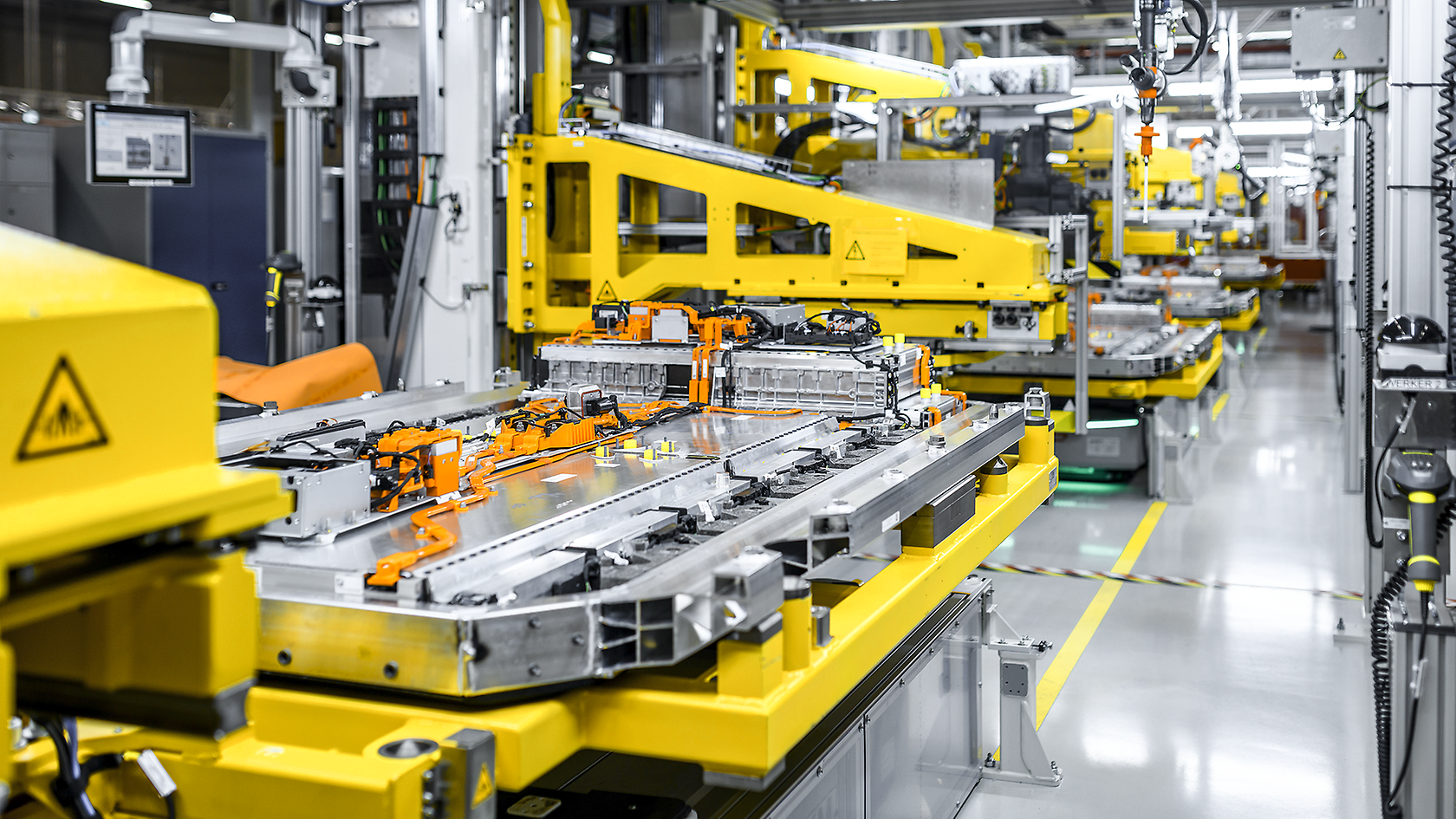
The opening of the Mercedes-Benz eCampus in July 2024 marks an important step in our sustainable business strategy. It is the competence centre for the development of cells and batteries for the future electric vehicles of the brand with the star. The activities of the eCampus form the starting point of the circular concept of Mercedes-Benz. With the "Design for Circularity" approach, the company views the entire value chain of battery technology from the start. From the development of new cell chemistry and the testing of battery cells to their production in small quantities for development, the company designs battery cells with Mercedes-Benz DNA. The findings flow into series production of the battery cells at partner companies.
Mercedes-Benz develops different forms of cell chemistry. Among other things, the company is working on lithium-ion cells with high-energy anodes based on silicon composites and innovative cobalt-free cathode chemistry as well as on solid battery technology. The aim is to develop the best possible cells with "Mercedes-Benz DNA" for a high energy density, rapid charging capacity and performance as well as to build up the know-how for their industrialisation.
The transformation to electromobility is our way of achieving the demanding carbon emission reduction targets throughout the entire life cycle. In this context, however, the energy requirement in the upstream supply chain increases. That is why our suppliers also play an important role within our holistic approach. Together with our partners in the supply chain, we want to implement effective climate protection measures. The goal: prevent, minimise or, as far as possible, end potential environmental impacts along the supply chain. Creating transparency is our starting point. In addition, we work with our partners to develop new sources of raw materials.
The net carbon-neutral
We address the carbon emissions in our supply chain via the "Ambition Letter ". For new contract awards, we only allow suppliers who have confirmed in writing that they will supply us with net carbon-neutral
In order to assess the sustainability performance of our direct suppliers, we have developed a comprehensive Supplier Ambition Rating in which we combine various methods for evaluating climate, environmental and human rights aspects.
The batteries for the electric Mercedes-Benz vehicles are produced in battery factories on three continents. Local battery production is a key success factor for the sustainable business strategy of Mercedes-Benz. Since 2022, Mercedes-Benz's own vehicle and powertrain production locations have been net carbon-neutral.

A large part of the carbon footprint of a battery-electric vehicle arises due to carbon containing charging processes. With Mercedes me Charge, we enable our customers to charge with green electricity
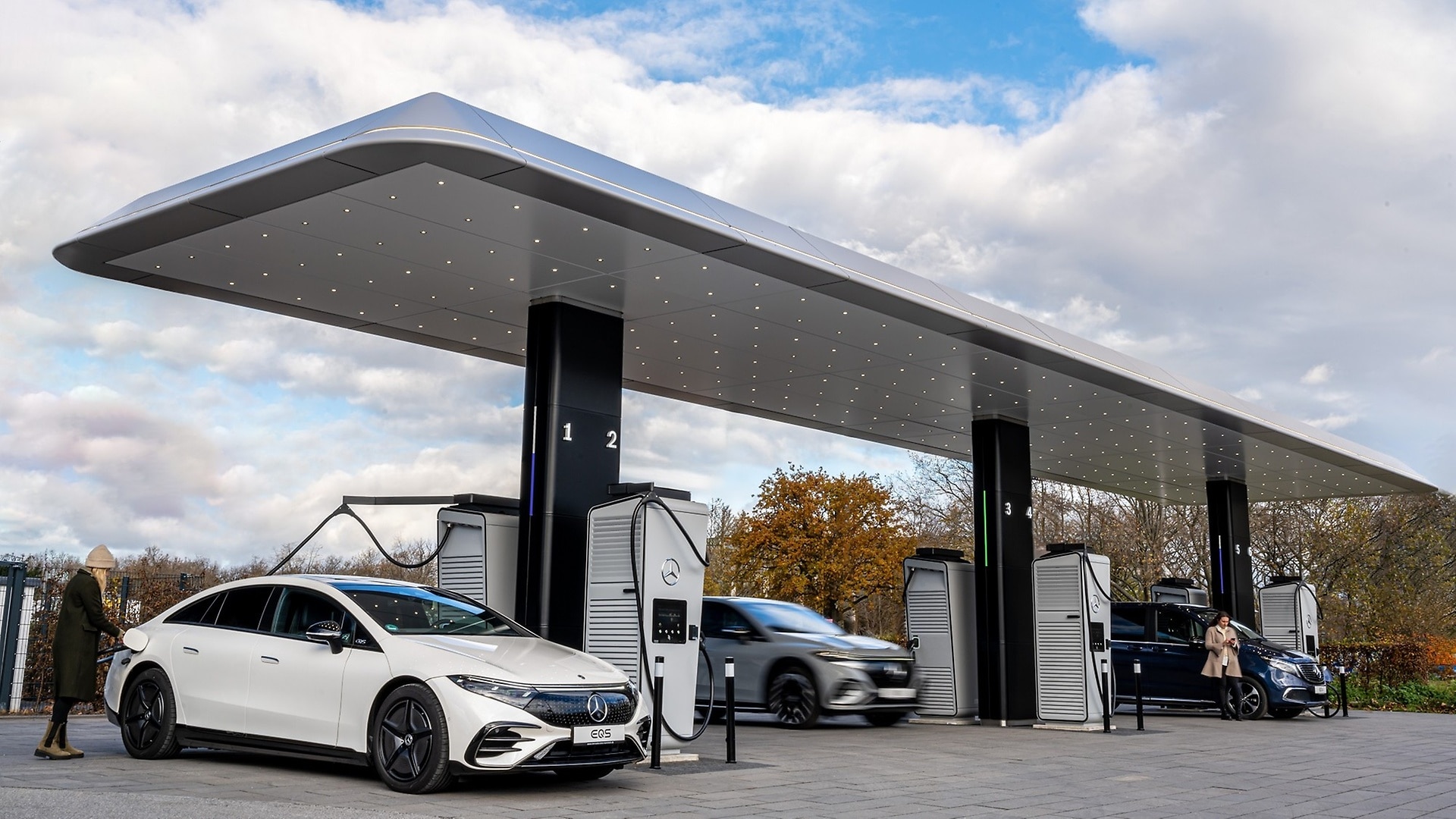

In line with our sustainable business strategy and the associated Ambition 2039, we will also offer our customers green charging
To promote the idea of a closed economic cycle and to conserve resources, we strive for reuse in the vehicle or repurpose of the battery before recycling. This allows raw materials and energy to be saved while reducing the amount of waste.
The company offers remanufactured batteries as replacement parts for all electric vehicles in order to live up to the idea of a circular economy and conserve resources. The function and quality of the repaired batteries are checked in detail in accordance with the series production specifications.
Even after their service life in vehicles, batteries offer considerable potential for reuse. With our subsidiary Mercedes-Benz Energy, we have established a successful business model with stationary large-scale storage applications. Batteries that can no longer be used in the vehicle can still be used in a 2nd-life-storage. In this way, we are improving the environmental performance of electric vehicles while also contributing to a more sustainable energy economy. Their energy storage systems can compensate for fluctuations in electricity production from renewable energy sources, smooth out load peaks and serve as backup power for an uninterrupted power supply. Some such energy storage systems are already in operation in Germany.

In our Mercedes-Benz Factory 56, for example, such a stationary power storage unit with a capacity of 1,400 kWh is in use. It stores solar power and releases it at night or on less sunny days.
In 2024, together with our partners GETEC ENERGIE and The Mobility House, we extended the service life of our energy storage units in Lünen and Elverlingsen, which have been in operation since 2016 and 2018, by another five years for primary control performance.
In a new project, Mercedes-Benz Energy supports the initiative of the Italian energy company Enel X to optimise the energy efficiency of Fiumicino airport in Rome through the use of reused vehicle batteries and thus reduce CO₂ emissions. It is planned to install Mercedes-Benz energy storage units with a total capacity of more than 5 MWh.
Material recycling is at the end of a battery's life. It forms the key for closing the recyclable material loop and is only used when the battery can no longer be reused or further utilised. In doing so, we are already able to fulfil far more than the recycling rates for drive batteries stipulated by the Battery Act. Battery housing, cables and busbars can be easily recycled. Battery modules in which most of the rare materials are installed are slightly more challenging. The goal is to further increase the recycling rates. The idea behind it: We use today's old batteries as a mine for the batteries of tomorrow.
The Mercedes-Benz battery recycling factory at our Kuppenheim site will cover all steps in battery quality from crushing and drying up to the processing of material flows. The planned process design of hydrometallurgy with recovery rates of more than 96 percent makes a real circular economy of battery materials possible. The integration of this innovative process into the overall concept of a recycling factory is currently unique in Europe. In China and the US, we work together with partners on battery recycling.

Mercedes-Benz is actively involved in the research and development of new recycling technologies and their establishment on the market. In addition, we participate in development and research projects and continue to drive forward the development of innovative technologies for the ecological and economic recycling of valuable raw materials.