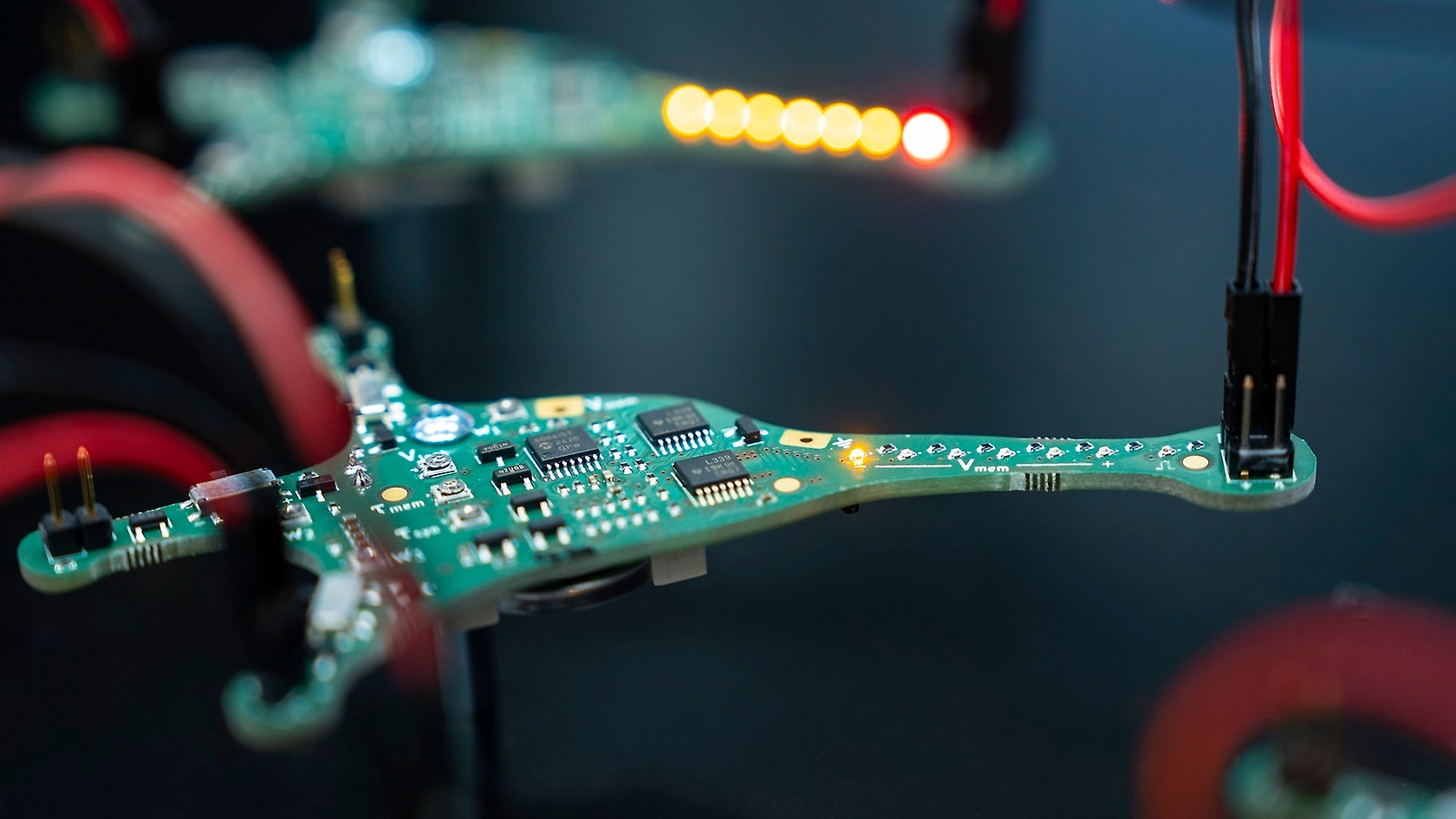
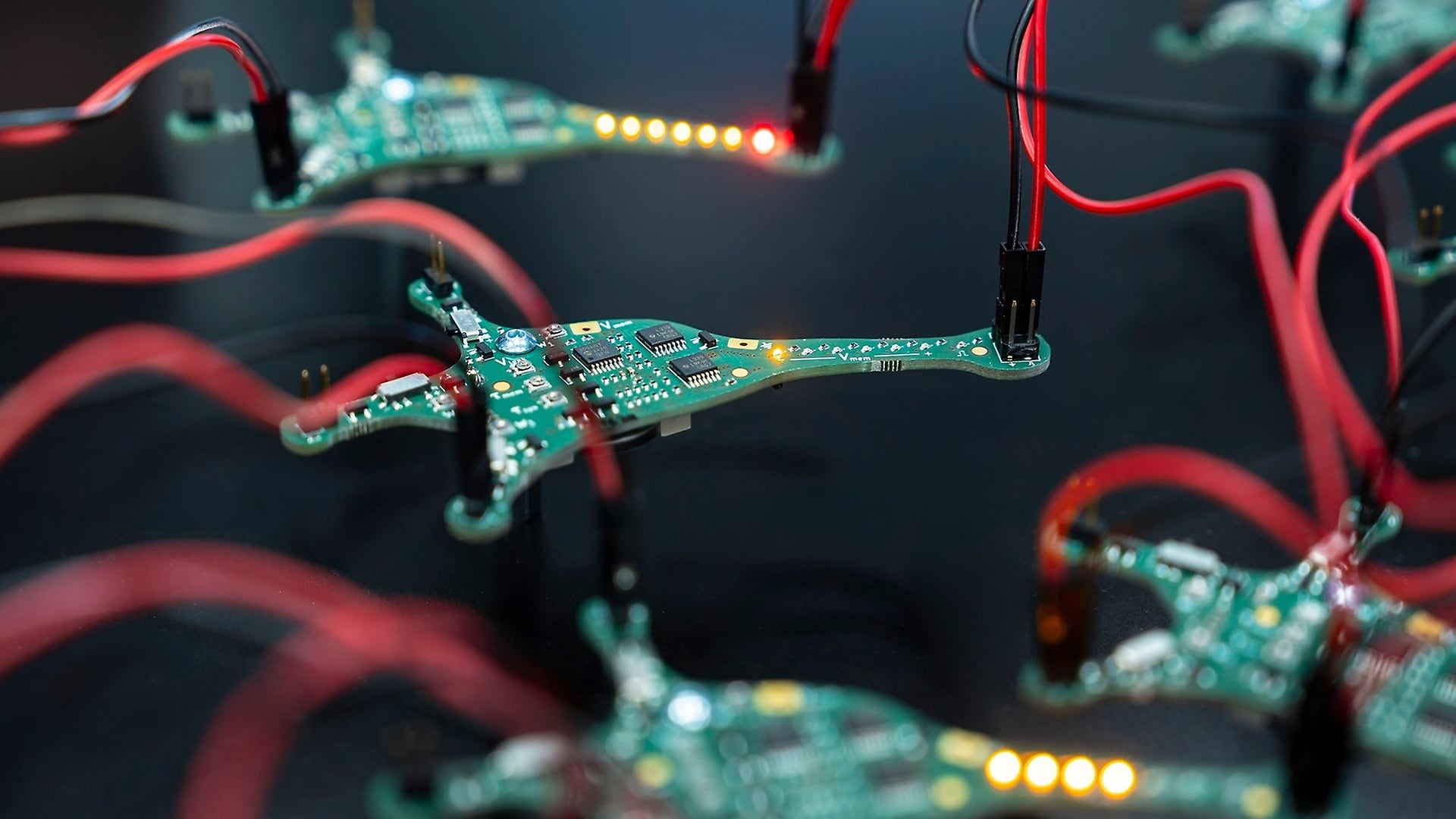
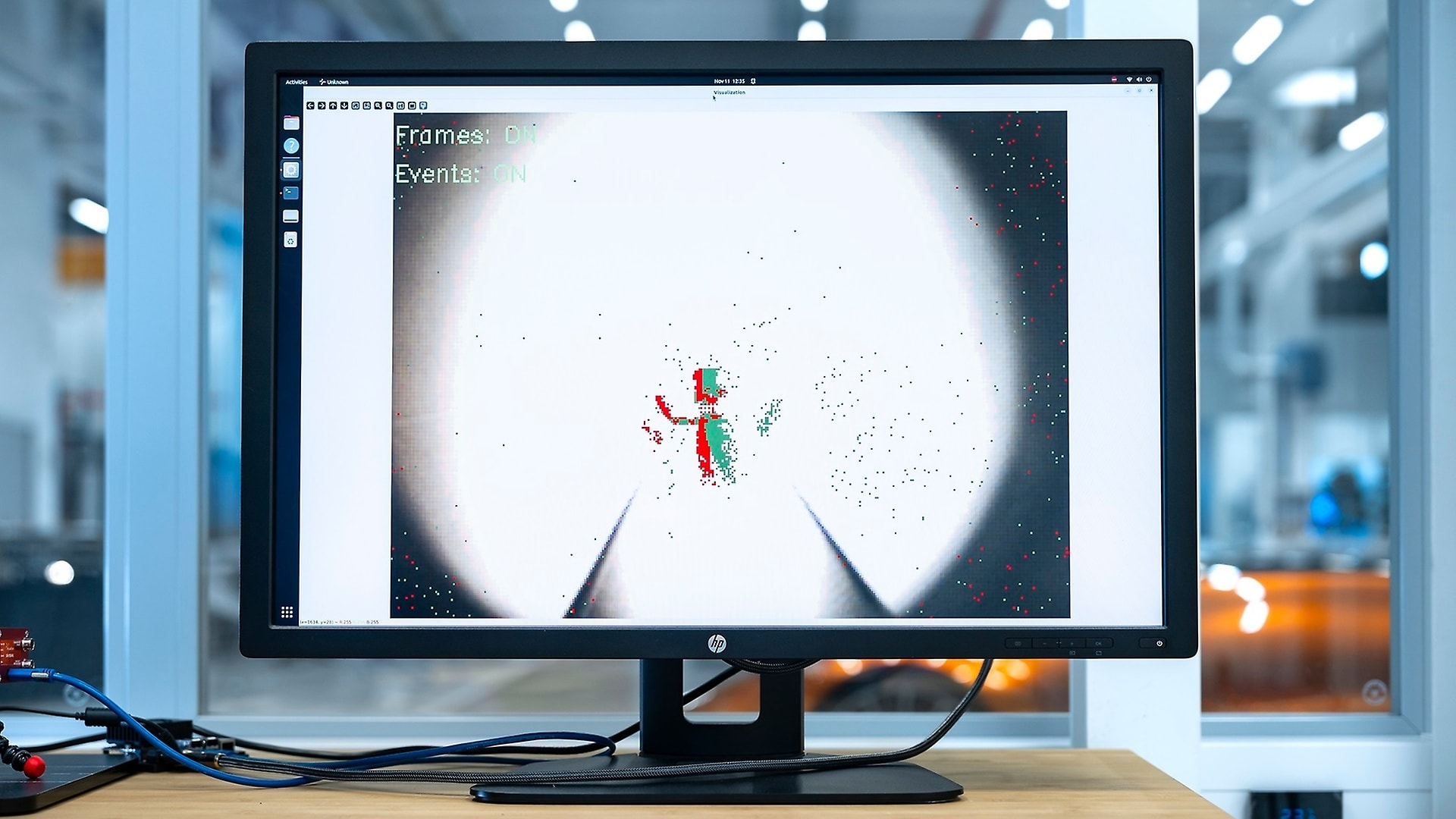
Safety systems could, for example, recognise traffic signs, lanes and other road users much better and react faster, even in poor visibility. And they could do so ten times more efficiently than current systems. There would be benefits in using a neuromorphic camera for interior monitoring, for example. Instead of full images (frames), it delivers individual pixels (events – hence the name event-based camera). The process is extremely fast with minimal delay. This means, for instance, a rapid system reaction to the blinking of a driver’s eye caused by fatigue. Neuromorphic computing has the potential to reduce the energy required for data processing in autonomous driving by 90 per cent compared to current systems.
,xPosition=0,yPosition=0.5)





,xPosition=0.8,yPosition=0)